Loading advertisement...
21-02-2025

The CBSE Class 12 Physics exam for 2025 was conducted on February 21, 2025, from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM. The question paper was well-structured, featuring a balanced mix of theoretical and numerical questions. Students described the exam as 'easy to moderate' in difficulty, with the numerical section being slightly tricky.
The CBSE Class 12 Physics exam was held on February 21, 2025, from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM. The paper consisted of 33 questions divided into different sections, testing both theoretical knowledge and numerical problem-solving skills. The total marks for the theory exam were 70, with an additional 30 marks allocated for practical assessments.
Teachers and students have shared their insights on the difficulty level of the Physics exam. Here’s a brief breakdown:
Difficulty Level: The exam was considered easy to moderate, with a balanced mix of theoretical and numerical questions.
Concept Coverage: The paper covered all major topics as per the CBSE syllabus, ensuring fair distribution across different units.
Numerical Questions: Some calculations were tricky, but overall, the numerical section was manageable.
Case-Based & Assertion-Reasoning Questions: These questions tested students’ conceptual understanding effectively.
Many students found the paper to be straightforward, while a few reported difficulty in specific numerical questions. The assertion-reasoning and case-study-based questions were a bit challenging but well within the expected pattern.
Subject experts believe that the paper was well-structured and aligned with CBSE’s guidelines. It followed the NCERT syllabus closely, making it easier for students who prepared thoroughly.
For practice and preparation, students can refer to previous years' CBSE Class 12 Physics question papers, which are available for download on educational websites. These papers provide insights into the exam pattern and types of questions asked in past years.
The CBSE Class 12 Physics exam 2025 was well-balanced and fair. Students who had a strong grasp of concepts and practiced numerical problems were able to attempt the paper confidently.
CBSE Class 12 physics Question Paper 2025 Set 1,2,3 PDF Download
| Question set | Link |
|---|---|
| Set -1 (55/6/2) | Click Here |
| Set -2 (55/2/2) | Click Here |
| Set -1 (55/2/1) | Click Here |
The CBSE Class 12 Physics Exam 2025 consists of a total of 33 questions divided into different sections based on marks distribution. Here’s the breakdown:
Set 1 (55/2/1)
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
1. Two charges -q each are placed at the vertices A and B of an equilateral triangle ABC. If M is the mid-point of AB, the net electric field at C will point along: (A) CA (B) CB (C) MC (D) CM | (B) CB |
2. A student has three resistors, each of resistance R. To obtain a resistance of (2/3)R, she should connect: (A) All the three resistors in the series (B) All the three resistors in parallel (C) Two resistors in series and then this combination in parallel with the third resistor (D) Two resistors in parallel and then this combination in series with the third resistor | (C) Two resistors in series and then this combination in parallel with the third resistor |
3. A 1 cm straight segment of a conductor carrying 1 A current in the x-direction lies symmetrically at the origin of the Cartesian coordinate system. The magnetic field due to this segment at point (1m, 1m, 0) is: 
| (C) |
4. The magnetic field due to a small magnetic dipole of dipole moment 'M' at a distance 'r' from the centre along the axis of the dipole is given by:  | (A) |
5. In the figure, X is a coil wound over a hollow wooden pipe. 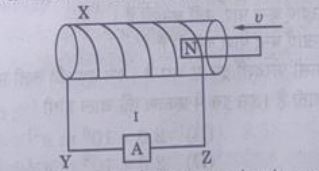 A permanent magnet is pushed at a constant speed v from the right into the pipe and it comes out at the left end of the pipe. During the entry and the exit of the magnet, the current in the wire YZ will be from: (A) Y to Z and then Z to Y (B) Z to Y and then Y to Z (C) Y to Z and then Y to Z (D) Z to Y and then Z to Y | (A) Y to Z and then Z to Y |
6. The alternating current I in an inductor is observed to vary with time t as shown in the graph for a cycle. Which one of the following graphs is the correct representation of the waveform of voltage V with time t? 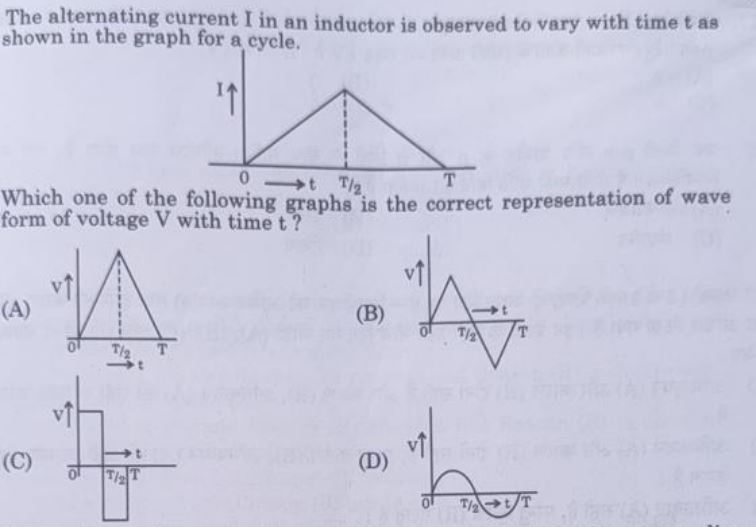 | (B) |
7. A transformer is connected to a 200 V AC source. The transformer supplies 3000 V to a device. If the number of turns in the primary coil is 450, then the number of turns in its secondary coil is: (A) 30 (B) 450 (C) 4500 (D) 6750 | (C) 4500 |
8. Which one of the following statements is correct? (A) Electric field due to static charges is conservative and field lines do not form closed loops. (B) Electric field due to static charges is conservative and field lines form closed loops. (C) Electric field due to static charges is non-conservative and field lines do not form closed loops. (D) Electric field due to static charges is non-conservative and field lines form closed loops. | (A) Electric field due to static charges is conservative and field lines do not form closed loops. |
9. A tub is filled with a transparent liquid to a height of 30.0 cm. The apparent depth of a coin lying at the bottom of the tub is found to be 16.0 cm. The speed of light in the liquid will be: (A) 1.6×108 m/s (B) 2.0×108m/s (C) 3.0×108m/s (D) 2.5×108m/s | (B) 2.0×108m/s |
10. Atomic spectral emission lines of the hydrogen atom are incident on a zinc surface. The lines which can emit photoelectrons from the surface are from: (A) Balmer series (B) Paschen series (C) Lyman series (D) Neither Balmer, nor Paschen, nor Lyman series | (C) Lyman series |
11. The energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom in the ground state is -13.6 eV. Its energy in an orbit corresponding to quantum number n is -0.544 eV. The value of n is: (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 | (D) 5 |
12. When the resistance measured between p and n ends of a p-n junction diode is high, it can act as a/an: (A) Resistor (B) Inductor (C) Capacitor (D) Switch | (C) Capacitor |
For Questions 13 to 16, two statements are given - one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below: (A) If both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A). 13. Assertion (A): In a semiconductor diode, the thickness of the depletion layer is not fixed. | (A) |
| 14. Assertion (A): In Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, the angular momentum of an electron in the nth orbit is proportional to the square root of its orbit radius rn. Reason (R): According to the Bohr model, an electron can jump to its nearest orbits only. | (C) |
15. Assertion (A): Out of infrared and radio waves, the radio waves show more diffraction effect. | (C) |
16. Assertion (A): In an ideal step-down transformer, the electrical energy is not lost. | (B) |
We will be updating the more answers soon...
Also visit: CBSE Class 10th Science Answer Key
CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exam 2025 Answer Key & Solutions